Explain Different Types of Electron Configuration
The p d and f orbitals have different sublevels. The four different types of orbitals spd and f have different shapes and one orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons.
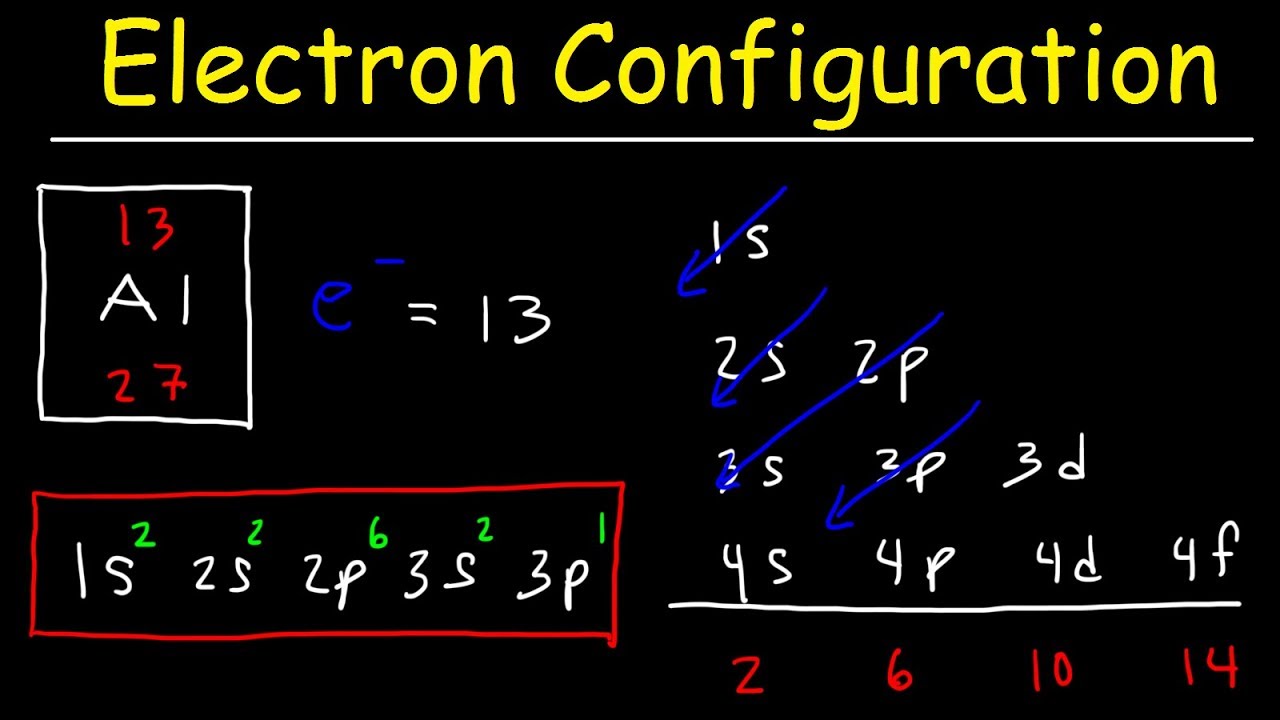
Electron Configuration Basic Introduction Youtube
111 rows The first examples of transition metals Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn are found in the fourth period even though the distinguishing electron in each case is a 3 d.
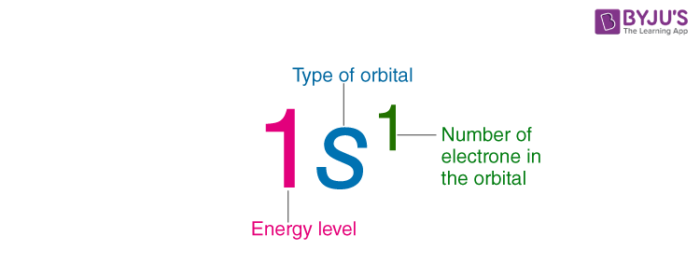
. In atomic physics and quantum chemistry the electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons in an atom molecule or other physical structure. In a more realistic model electrons move in atomic orbitals or subshells. The 15 electrons of the phosphorus atom will fill up to the 3 p orbital which will contain three electrons.
Help explain the properties of elements and the structure of the periodic table. For example the electron. The p d and f orbitals have different sublevels thus can hold more.
Electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule or other physical structure in atomic or molecular orbitals. An ion of an atom is one in which the number of protons and electrons is not the same. Electron Configurations are an organized means of documenting the placement of electrons based upon the energy levels and orbitals groupings of the periodic table.
1s 2 2s 2. The M shell in this example is the valence shell. The electrons occupying the outermost shell orbital s highest value.
The last electron added is a 3 p electron. This electron must go into the lowest-energy subshell available the 3 s orbital giving a 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 6 3 s 1 configuration. The s or p tell us the.
The Complete Electron Configurations Concept Builder challenges learners to recognize the electron configuration for the atoms and the ions of. When atoms collide and react it is the outer electrons that meet and. 119 rows ELECTRON CONFIGURATION.
The four different types of orbitals spd and f have different shapes and one orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. There are four different orbital shapes. Krypton has two 1 s electrons two 2 s electrons six 2 p electrons two 3 s electrons six 3 p electrons two 4 s electrons ten 3 d electrons and six 4 p electrons.
Within each shell the s subshell is at a lower energy than the p. 1s 2 2s 1. Here is a summary of the types of orbitals and how many electrons each can contain.
Therefore n 3 and for a p -type orbital l. The electron configurations of silicon 14 electrons phosphorus 15 electrons sulfur 16 electrons chlorine 17 electrons and argon 18 electrons are analogous in the electron. S p d and f.
Electron Configurations of Second-Period Elements. The electron configuration describes where the electrons are inside orbitals. The electronic configuration of each element is decided by the Aufbau principle which states that the electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy levels.
So based on what we know about the quantum numbers and using the chart above you need 2 electrons. The electron configurations of silicon 14 electrons phosphorus 15 electrons sulfur 16 electrons chlorine 17 electrons and argon 18 electrons are analogous in the electron configurations of their outer shells to their corresponding family members carbon nitrogen. The structure of the Periodic table of elements is partly based on electron configuration.
There are four kinds of. The electronic configurations of atoms. The 11 electrons are distributed with 2 electrons in the K shell 8 electrons in the L shell and 1 electron in the M shell.
If there are more protons than electrons an atomic ion has a positive charge and is.

Electron Configuration Detailed Explanation Filling Of Orbital Representation Of Electronic Configuration Of Atom With Faqs
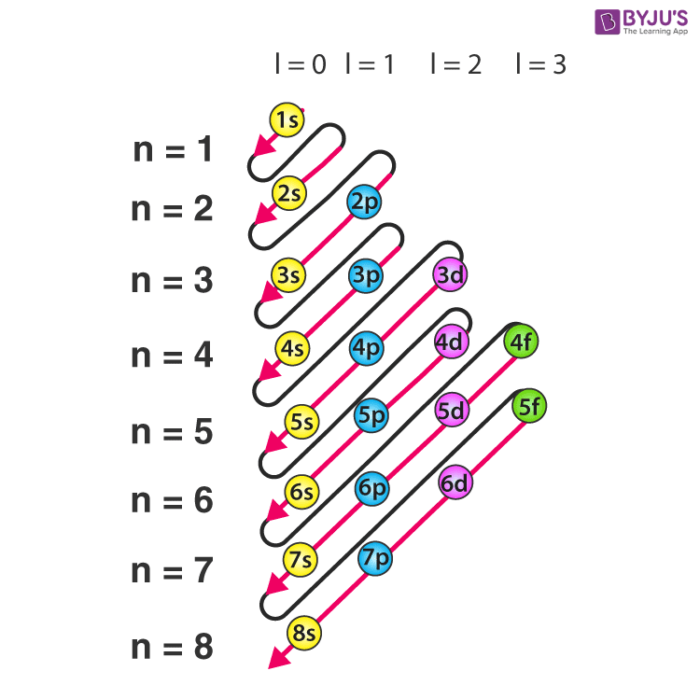
Electron Configuration Detailed Explanation Filling Of Orbital Representation Of Electronic Configuration Of Atom With Faqs

Comments
Post a Comment